BALLIOL COLLEGE, SPORTS PAVILION
NOVEMBER 2019

7:45 AM, London Bridge. The train from Uckfield just entered the station and is spitting out hundreds of commuters, flowing past us. We hop on the now empty train and leave London to visit our timber sub-contractor’s workshop in East Sussex.
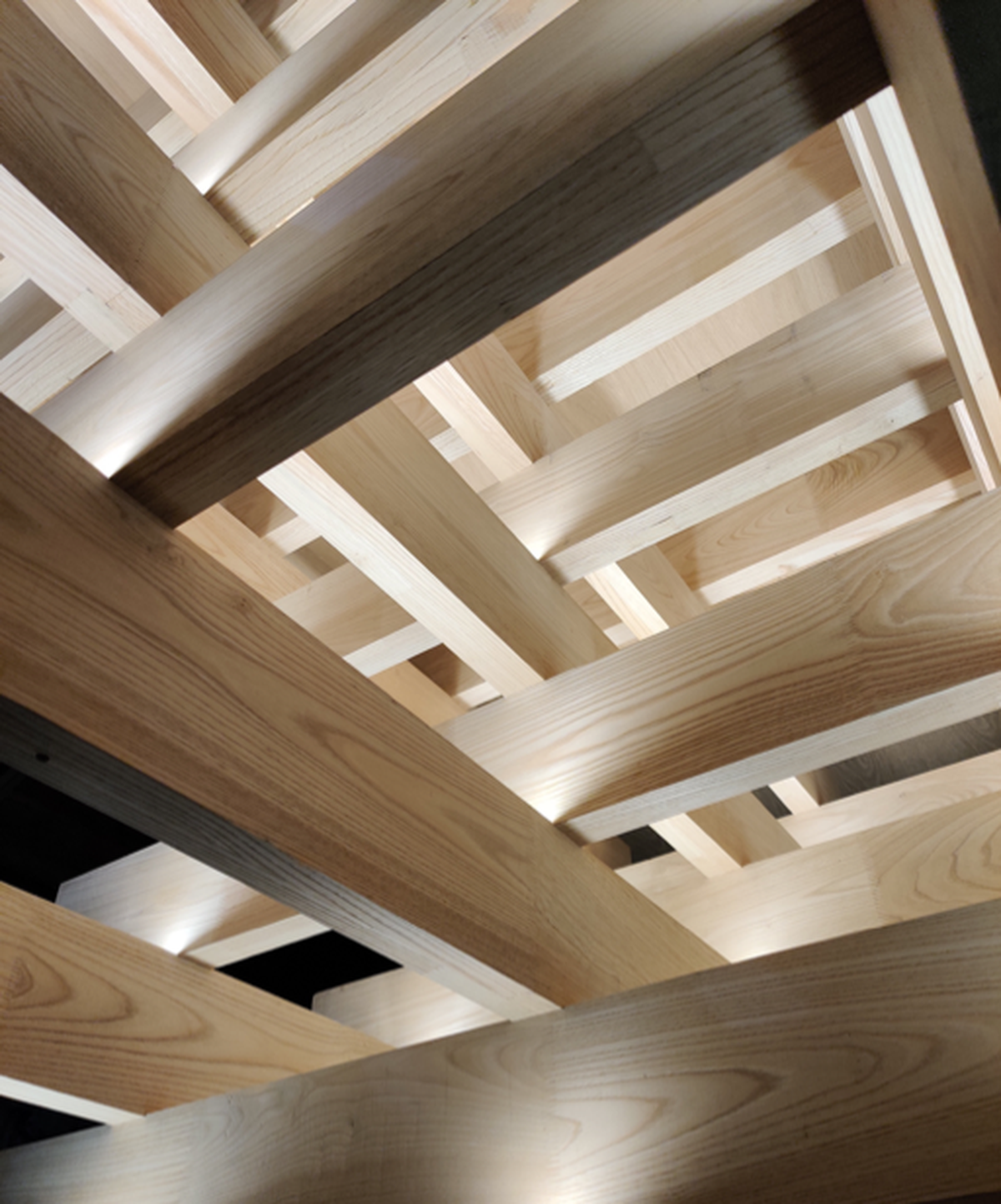
We are fast approaching the construction stage of our Sports Pavilion project for Balliol College in Oxford and were invited to review a mock-up of the roof structure. The pavilion roof is formed of slender sweet chestnut glulam joists; 10 layers are stacked on top of each other, each layer cantilevering further into the space, creating a coffer.

1:50 model
From outside the roof structure expresses itself as a lantern, popping up in the centre of the building. The lantern is fully glazed, allowing for rays of sunshine to enter through the stacked glulam. In the evening, the dense timber lattice will be highlighted by a subtle glow, originating from LED strips, that are recessed in the top of the glulam joists.
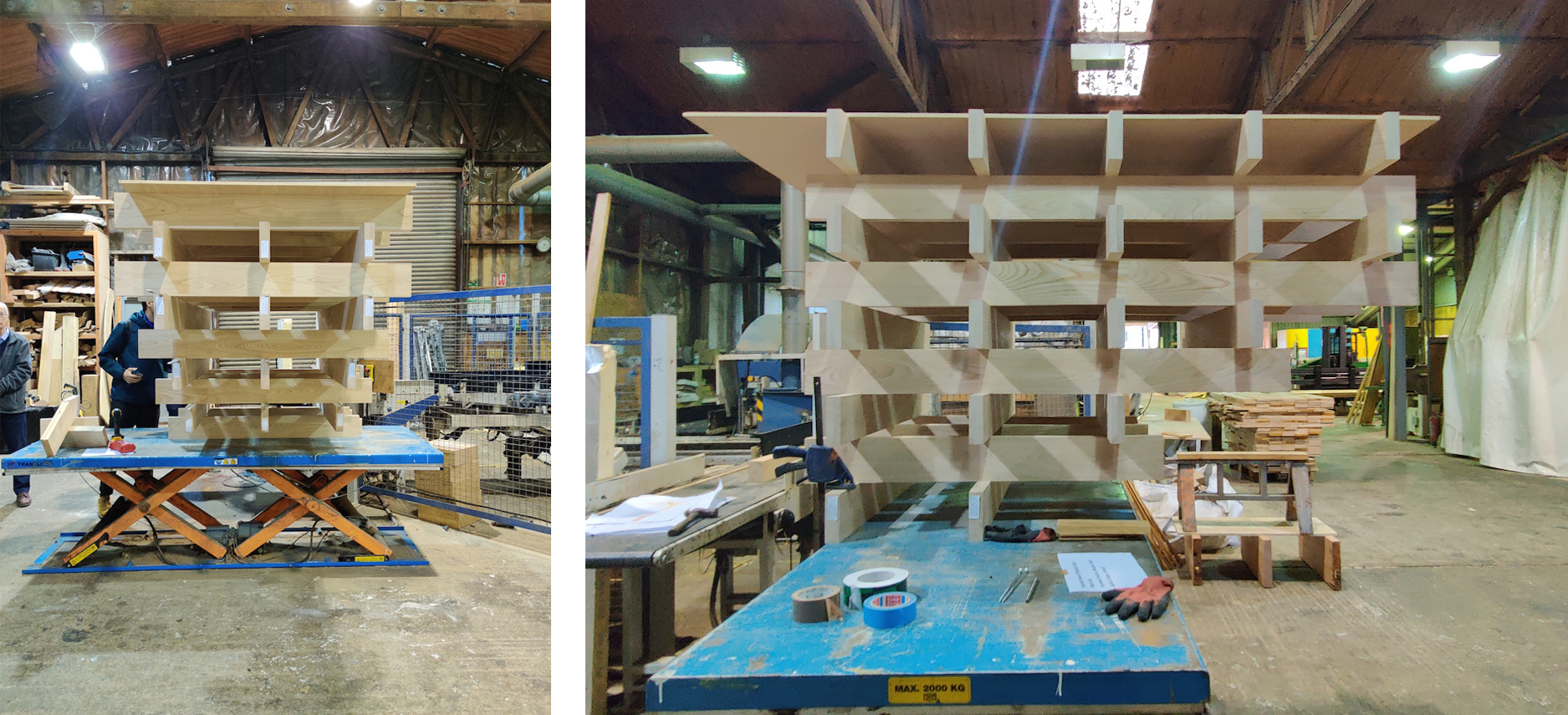

The mock-up in Inwood’s (timber sub-contractor) workshop


Lighting strategy detail plan and section
The mock-up was used to test the connection details between the individual layers of glulam, the construction sequence, and the integration of the LED strips and the associated wiring. Preceding the assembly of this mock-up, these details have been worked through and coordinated in many lengthy design workshops, involving the contractor, structural and electrical engineers, the timber sub-contractor, electricians and us architects. As such, it was even more enjoyable to review the mock-up with all the parties involved and to see our combined efforts bearing fruit.
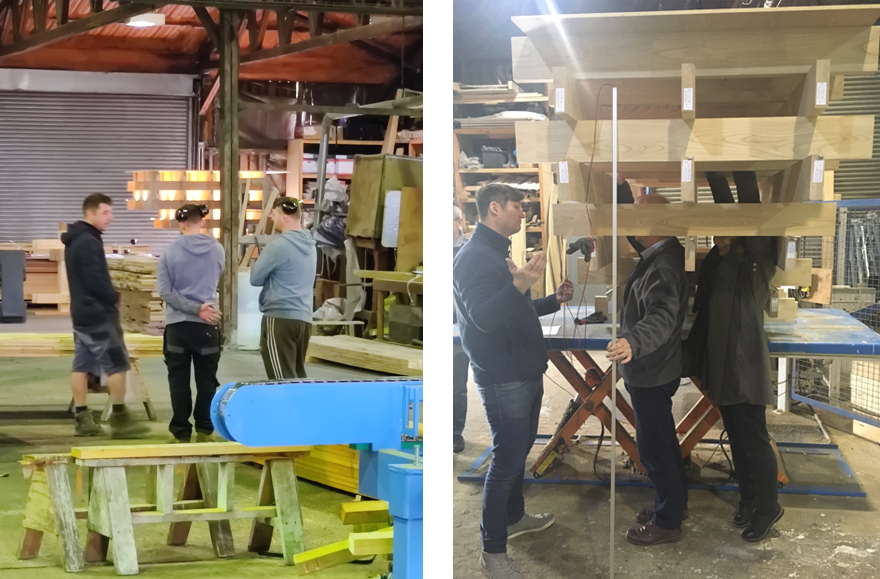

The carpenters who built the mock-up and the Electrical Engineer, Design Manager, and Architect discussing the installation and accessibility of the LED strips
MASTER’S FIELD PROJECT
APRIL 2019
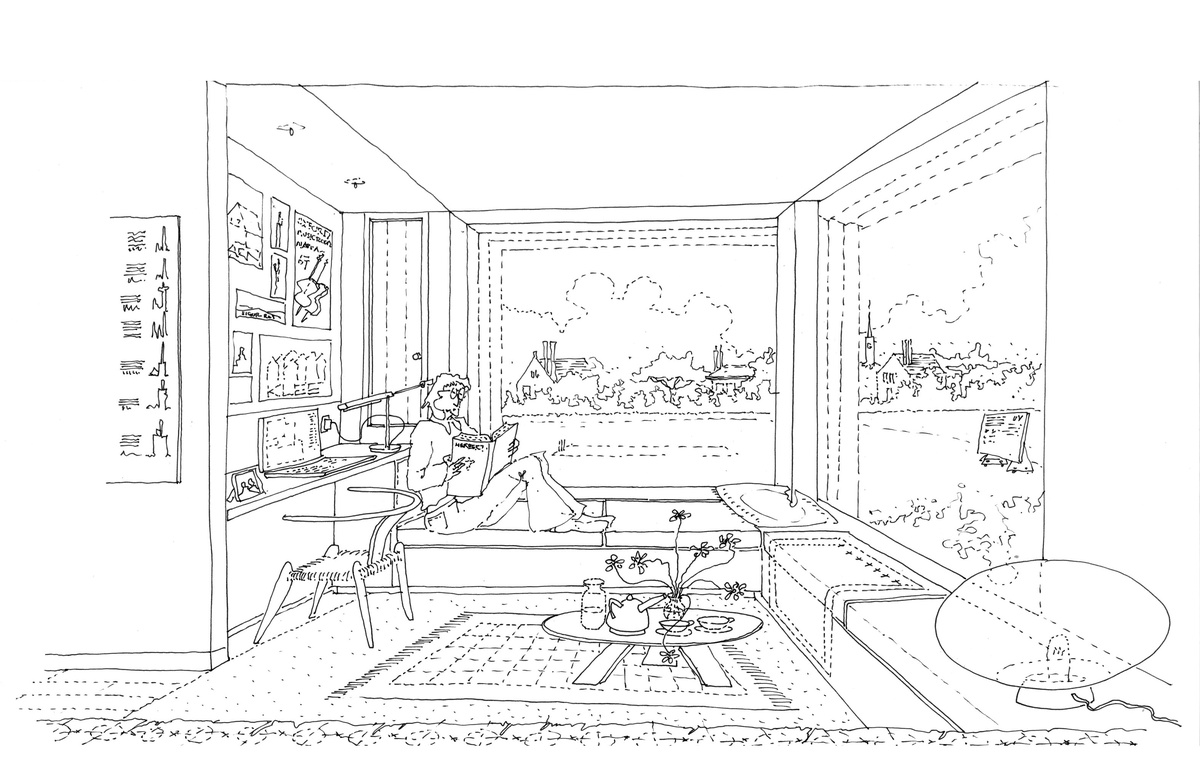
When reflecting on the work of our practice, the chamfered corner, is a recurring interest. This detail has developed over the years from our preoccupations with the Miesian re-entrant corner, the simplicity of a trabeated structure, and a desire to find ways of expressing a deep façade.
Simple chamfers in concrete and stone were employed in recent completed projects for Hampshire House and The Sultan Nazrin Shah Centre, Oxford. At the Master’s Field site in Oxford, currently under construction for Balliol College, a corbelled chamfered detail is incorporated in a load bearing façade. This project comprises eight student accommodation buildings and a pavilion arranged around a series of courtyards overlooking a cricket pitch.

A brick-clad chamfer at the corner between two windows is used throughout the accommodation buildings. This establishes a shifting perspectival relationship as one moves through the site, and gives all the buildings a common language. Corbelled brick and concrete lintels and mullions set up a trabeated structural rhythm which clearly defines each individual student bedroom and creates a delicate play of light and shadow across the façade. A series of finely detailed brick and concrete panels are layered within the depth of the window reveal, articulating a secondary rhythm which expresses the transition from solid to glazed elements.
The detail enables the depth and structure of the wall to be elegantly expressed, maximizing its presence when viewed externally and minimizing its presence internally. It also forms a generous threshold which provides privacy for students inside engrossed in their study. For moments of welcome distraction, the large picture windows frame uninterrupted views over the cricket pitch and across the campus.
The expression of a chamfered corner produces challenges in construction, particularly when expressed in precast concrete components clad in corbelled brickwork. When forming acute angles with orthogonal bricks, special consideration must be given to alignments and bonding. Interface details demand careful thought regarding sequencing and tolerances to achieve a symbiosis of structural performance with aesthetic ambition.
Externally, in the plan detail shown here, the apex of the chamfer is formed from stacked brick headers. This exposes three faces of each brick, limiting the choice of bricks, which are typically produced with only one finished stretcher face. Brick specials are required to form the chamfered corbel of the lintels, and grids are carefully set out to ensure alignment of vertical and horizontal corbelling. We looked to the meticulously detailed and crafted brickwork of Jensen-Klint’s masterpiece, Grundvig’s Church in Copenhagen, for expression of stepped vertical forms.
Internally, minimising the corner where the windows meet produces intricate challenges in the alignment of linings, blinds, reveals and fitted furniture. This complex resolution of constituent parts all work hard to achieve the aesthetic objective of the simple glazed chamfered corner.

Detail Key
1.Whitewashed ply bench 2. Aluminium window 3.Whitewashed plywood reveal 4.Plasterboard 5.Rigid insulation 6.Steel window fixing brackets 7.Metal pressing 8.Wind post 9.EPDM/ vapour barrier 10.Mineral wool insulation 11.Breather membrane 12.Steel restraint brackets 13.Corbelled brick faced precast concrete mullion 14.Flashing 15.Concrete cill 16.Concealed curtain track 17.Oak joist over 18.Concealed roller blind 19.Timber panels 20.Timber framed window 21.Prelaminated timber frame 22.Precast concrete mullion 23.Precast concrete coping over








